professional manual blood pressure cuff
Professional manual blood pressure cuffs are essential tools for accurate BP measurement, utilizing a cuff, sphygmomanometer, and stethoscope to ensure reliable results in clinical settings, offering durability and precision preferred by healthcare professionals.
Overview of Manual Blood Pressure Measurement
Manual blood pressure measurement involves using a cuff, sphygmomanometer, and stethoscope to assess systolic and diastolic pressures. The process requires inflating the cuff above the elbow, then deflating it slowly while listening to arterial sounds. Proper technique ensures accurate readings, crucial for diagnosing hypertension and monitoring cardiovascular health. Regular use in clinical settings highlights its reliability and importance in patient care, emphasizing the need for correct cuff sizing and a quiet environment to minimize errors and ensure precise results consistently.
Importance of Accuracy in Blood Pressure Monitoring
Accuracy in blood pressure monitoring is crucial for obtaining reliable data, enabling proper diagnosis and treatment. Incorrect measurements due to improper cuff size or technique can lead to misdiagnosis or inappropriate therapy. Ensuring precise readings is vital for assessing hypertension, preventing complications, and maintaining patient trust in clinical care. Accurate monitoring also aids in early detection of cardiovascular issues, emphasizing the need for standardized methods and trained professionals to ensure consistent and reliable results.
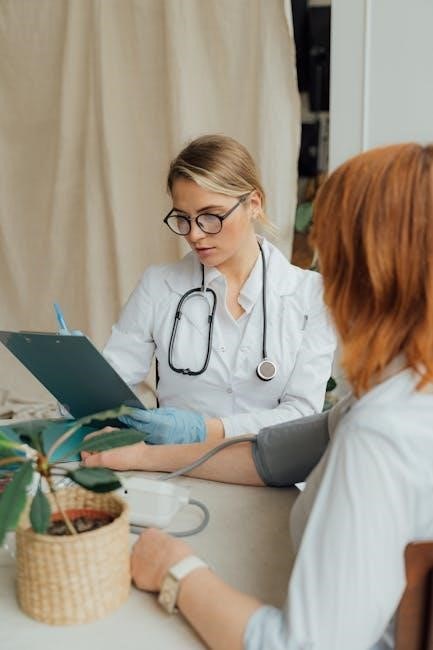

Components of a Professional Manual Blood Pressure Cuff
Professional manual blood pressure cuffs consist of a durable cuff, a sphygmomanometer for pressure measurement, and a stethoscope for heart sounds, ensuring accurate BP readings.
The Cuff and Its Design
The cuff is a crucial component, designed to encircle the upper arm, typically made of durable, flexible material. Proper fit is essential, with the cuff’s WIDTH covering 40% of the arm’s circumference and the length extending to the upper arm. A D-ring or Velcro closure secures it in place. The cuff wraps snugly around the arm, ensuring even distribution of pressure for accurate readings. Its design includes an inflation bladder and an adjustable strap for a secure fit. Sizes vary to accommodate different arm circumferences, ensuring comfort and accuracy in blood pressure measurement. Proper cuff size is vital to avoid errors in readings, emphasizing the importance of correct fit. The cuff’s material is chosen for longevity and ease of cleaning, making it suitable for repeated clinical use. Additionally, the cuff’s design allows for easy deflation after measurement, ensuring patient comfort. The combination of functionality and comfort in the cuff’s design makes it an indispensable tool in professional blood pressure monitoring.
The Sphygmomanometer and Its Function
The sphygmomanometer is a manual device essential for measuring blood pressure, consisting of an inflation bulb and a gauge. It works by inflating the cuff to occlude the artery and gradually deflating it, allowing the detection of Korotkoff sounds through a stethoscope. Available in mercury and aneroid types, with mercury being the gold standard but less used now, it provides precise readings crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment in clinical settings.
The Role of the Stethoscope in Manual Measurements
The stethoscope is crucial for detecting Korotkoff sounds during manual blood pressure measurement. It allows healthcare providers to listen to the arterial sounds as the cuff deflates. Ensuring accurate placement and using high-quality stethoscopes minimizes external noise interference. Proper usage of the stethoscope ensures precise systolic and diastolic readings. Regular maintenance of the stethoscope ensures optimal performance, making it an indispensable tool in accurate blood pressure monitoring.

Advantages of Using a Manual Blood Pressure Cuff
Manual blood pressure cuffs offer precision, reliability, and cost-effectiveness, making them a preferred choice for healthcare professionals. They ensure accurate readings without reliance on batteries.
Accuracy and Reliability in Clinical Settings
Manual blood pressure cuffs are renowned for their precision in clinical environments, delivering consistent results when used correctly. Unlike automated devices, manual cuffs eliminate errors from movement or improper placement, ensuring accurate readings. Their reliability stems from the direct control over cuff inflation and deflation, allowing healthcare professionals to assess systolic and diastolic pressures precisely. This method is particularly trusted in settings requiring high diagnostic accuracy, solidifying its role as a cornerstone in medical practice.
Cost-Effectiveness and Durability
Manual blood pressure cuffs are a cost-effective option for healthcare professionals, offering long-term durability and minimal maintenance. Unlike automated devices, they lack electronic components, reducing the risk of mechanical failure; Their robust design ensures a long lifespan, making them a practical investment for frequent use. Additionally, manual cuffs are often more affordable than digital monitors while maintaining high accuracy, making them a preferred choice for both clinical and home settings.
How to Use a Professional Manual Blood Pressure Cuff
To use a professional manual blood pressure cuff, ensure a quiet environment, place the cuff on the bare upper arm, inflate above systolic pressure, and use a stethoscope to detect sounds. Deflate slowly and record the readings accurately for reliable results.
Preparing for Measurement
Before measuring blood pressure, ensure a quiet and comfortable environment. Sit comfortably with your back straight, feet flat on the floor, and arm resting at heart level. Remove tight clothing from the upper arm and avoid talking or moving during measurement. Place the cuff on the bare upper arm, ensuring proper fit and alignment with the artery. Check the cuff size to match the arm circumference, and ensure the sphygmomanometer is at zero. Relax for a few minutes before starting the measurement for accurate results.
Step-by-Step Measurement Process
Place the stethoscope over the brachial artery, then inflate the cuff 30-40 mmHg above the systolic pressure. Slowly deflate the cuff while listening for the first Korotkoff sound, noting the systolic pressure. Continue deflating until the sounds disappear, marking the diastolic pressure. Record both readings accurately. Ensure the cuff deflates completely between measurements and allow a 1-2 minute interval if re-measuring. Proper technique is crucial for obtaining reliable and precise blood pressure readings.

Tips for Choosing the Right Cuff Size
Selecting the correct cuff size is crucial for accurate readings. Measure arm circumference and choose a cuff with an appropriate range. Proper fit ensures reliable results and comfort during measurement.
Measuring Arm Circumference
Measuring arm circumference accurately ensures proper cuff fit. Use a flexible tape measure to wrap around the midpoint of the upper arm, one inch above the elbow bend. Record the circumference to select a cuff size that matches the range. This step is vital for ensuring accurate blood pressure readings and avoiding errors caused by an ill-fitting cuff. Proper measurement guarantees comfort and reliability during the monitoring process.
Ensuring Proper Fit for Accurate Readings
Ensuring proper fit is crucial for accurate blood pressure readings. The cuff should be snug but not overly tight, with the INDEX line aligned with the arm’s midpoint. If the cuff is too small, it may overestimate readings, while a cuff that’s too large can underestimate them. Always verify that the arm circumference falls within the cuff’s designated range for optimal accuracy and comfort during measurement. Proper fit minimizes errors and ensures reliable blood pressure monitoring.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Common challenges include cuff size errors and environmental noise, which can affect accuracy. Using the correct cuff size and ensuring a quiet environment help overcome these issues effectively;
Overcoming Cuff Size Errors
Cuff size errors are a common issue, leading to inaccurate blood pressure readings. To address this, ensure the cuff is appropriately sized for the patient’s arm circumference. The cuff’s INDEX line should align with the midpoint of the upper arm. Using a cuff that is too small or too large can result in incorrect measurements. Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for proper sizing. Regularly checking and adjusting the cuff size helps maintain measurement accuracy and reliability in clinical settings.
Addressing Environmental Factors
Environmental factors significantly impact blood pressure measurements. Ensure the setting is quiet and free from distractions to minimize stress-induced fluctuations. Maintain a comfortable room temperature and avoid drafts. Patients should rest for at least five minutes before measurement and avoid caffeine or nicotine. The healthcare provider should also ensure the patient is seated comfortably with their arm supported at heart level. Proper environmental preparation helps achieve accurate and reliable blood pressure readings, reducing variability and ensuring consistent results in clinical and home settings.

Maintenance and Storage Best Practices
Regularly clean the cuff with mild soap and water, avoiding harsh chemicals. Store in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture to maintain durability and functionality.
Cleaning and Storing the Cuff
Cleaning and storing the cuff properly ensures longevity and accuracy. Use mild soap and warm water to gently wipe the cuff, avoiding harsh chemicals or abrasive materials. Rinse thoroughly and air dry. Store the cuff in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. Avoid folding or creasing the cuff, as this can cause damage. Regular cleaning prevents bacterial growth, maintaining hygiene and ensuring precise measurements.
Calibrating the Sphygmomanometer
Calibrating the sphygmomanometer ensures accurate blood pressure readings. Use a calibration kit or a mercury manometer as a reference. Inflate the cuff to the recommended pressure and compare the readings. Adjust the device according to the manufacturer’s instructions until the measurements match. Regular calibration, ideally every 6-12 months, is essential to maintain precision. Always have the device calibrated by a trained professional to guarantee reliability in clinical settings. Proper calibration prevents errors and ensures consistent, trustworthy results.
