Accident analysis and prevention pdf
Read the latest articles of Accident Analysis & Prevention at ScienceDirect.com, Elsevier’s leading platform of peer-reviewed scholarly literature
64 V. Dixit et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 62 (2014) 63–78 gap in the light of this or whether the critical gap is decided by the risk
J. Duke et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 42 (2010) 364–371 365 1. Introduction The transport and storage industry plays a significant role in a
138 A. Macmillan et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 86 (2016) 137–145 of the UK remain lower than those in many European countries (Gatrell,
288 W.J. Curnow/Accident Analysis and Prevention 35 (2003) 287–292 consequent focal injury to the brain might have been tested if the requisite data had been collected, but the study shows
102 M.S. Horswill et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 52 (2013) 100–110 1.5. Can hazard perception be improved through training? Hazard perception ability appears to be susceptible to reme-
1408 R.A. Lyons et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 40 (2008) 1406–1410 EDdatafromoneEnglishhospitalwerealsomatchedwithlocal
Recently published articles from Accident Analysis & Prevention.
R. Li et al./Accident Analysis and Prevention 75 (2015) 192–201 193 mixture models in analyzing and predicting incident data has not been indicated in the literature.
all its aspects: for example, the prevention of occupational accidents and diseases, a wider application of the principles of ergonomics, the arrangement of working time, …
E. Minikel / Accident Analysis and Prevention 45 (2012) 241–247 243 Berkeley’s bicycle boulevards are safer for cyclists, both in terms of collision rate and severity, than the arterials to which they run
J. Wang et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 84 (2015) 54–64 55 significantly associated with accident severity. These studies pro-vided
M.A. Griffin et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 68 (2014) 156–171 157 for operating effectively in both predictable and unpredictable environments,
accident analysis for more than 20 years, there have only been a few attempts of formalising the concept and of developing systematic classifications of barriers. After reviewing the main prior treatments of the barrier concept, a systematic
54 Z. Li et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 64 (2014) 52–61 Fig. 2. Speed contour for the study segment (mph): Wednesday, October 24th, 2007; time and space are shown on the x- and y-axes, respectively, and the color scale
828 P. Konstantopoulos et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 42 (2010) 827–834 that although night driving conditions have little effect on periph-
Walking is a popular form of physical activity associated with clear health benefits. Promoting safe walking for pedestrians requires evaluating the risk of pedestrian-motor vehicle collisions at
X.S. Dong et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 102 (2017) 136–143 137 ture appearstolackascientificreviewoffallsfromheight(Nadhim et al., 2016).
Accident Analysis and Prevention daneshyari.com

Accident Analysis and Prevention SFU.ca
author’s knowledge, driver hazard perception is rarely considered in the evaluation on the crash avoidance effect of FCATs in early stages of
S.H. Hamdar, J. Schorr / Accident Analysis and Prevention 55 (2013) 22–33 23 33,000 Uninterrupted fatalitiesin2009andalthoughthisisadecreaseinbothtotal
302 L. Carnis, E. Blais / Accident Analysis and Prevention 51 (2013) 301–309 describes themethodologyusedwhilethelasttwosectionspresent and discuss the results.
Rear seat safety:Variation inprotection by occupant, crash and vehicle characteristics Dennis a R. Durbina,b,c,*, Jessica S. Jermakianc, Michael J. Kalland, Anne T
156 F. Abdat et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 70 (2014) 155–166 Haslam and Bentley (1999) had already observed that a combina-tion of slippery conditions, use of footwear with worn treads and
2 J. de O˜na et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 51 (2013) 1–10 results showed that the clustered data provided information that would not have been obtained if only the full database had been

7 Preface This book is about safety analysis as a tool for accident prevention. The methods can be used to analyse systems and to investigate accidents, and
1482 A.D. Wright, A.C. Laing / Accident Analysis and Prevention 43 (2011) 1480–1487 Table 1 Photos and characteristics of the five floor conditions tested in this study.
360 H.R. Marucci-Wellman et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 98 (2017) 359–371 Over the past two decades we have completed several studies
prevention by collection and analysis of safety data and by a prompt exchange of safety information , as part of the State safety programme. Accident prevention measures 4 Accident prevention measures. 5 1. State safety policy and objectives 1.1 State safety legislative framework 1.2 State safety responsibilities and accountabilities 1.3 Accident and incident investigation 1.4 Enforcement
UNCORRECTED PROOF Please cite this article in press as: Hatfield, J., Fernandes, R., The role of risk-propensity in the risky driving of younger drivers.
V. Dixit, T.H. Rashidi / Accident Analysis and Prevention 70 (2014) 140–147 141 Unlike most crash datasets in which only information of people
M.A. Figliozzi, C. Tipagornwong / Accident Analysis and Prevention 96 (2016) 169–179 171 cation, unlike mass media campaigns, entails lessons or seminars
PDF The issue of seat belt use in middle- and low-income countries is strongly evident and has as a result higher rates of fatalities and seriously injured on the roads. The first systematic
D.M. Sanbonmatsu et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 92 (2016) 22–33 23 purpose of our study was to explain the hypocrisy of drivers using
272 A.B. Ünal et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 48 (2012) 271–278 a high processing demand, indicating the music was influencing driving

38 Y. Xie et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 47 (2012) 36–44 Fig. 1. Definition of points of impact. It can be seen that the class probability Prob(class=m) is also
Highly correlated variables in a regression analysis leads to regression coefficients with a large standard error, thus making it difficult or impossible to determine the influence of individual
arbitrary data sets as combination of points in a larger dimensional space. It uniquely simplifies complex data into knowledge extraction in a completely different way than parametric estimation does.
42 R.Q. Ivers et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 86 (2016) 40–46 Table 1 Reliability of the self-reported attitude, behaviour, and motivation scales.
2 Editorial / Accident Analysis and Prevention 44 (2012) 1–2 Fig. 1. Distribution of road deaths by road user group in EU capital cities, based on the average values for 2004–2006, and ranked by the share of pedestrians and cyclists
2 X. Liu et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 98 (2017) 1–9 gle parameter, FRA track class, might not satisfactorily account for all thepertinentfactors
Accident Analysis and Prevention Curtin University
S. Lenton et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 42 (2010) 637–644 639 designed for this project. This was followed by a semi-structured qualitative interview exploring their experiences of and atti-
26 I. Tournier et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 91 (2016) 24–35 the risk of getting lost and the anxiety that ensues (Phillips et al., 2013).
908 K.A. Brookhuis et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 43 (2011) 906–910 Table 1 Average scores per condition on the performance variables of the tests.
26 D.J. Myers et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 68 (2014) 25–29 considered notculture.Therefore,wesuggestthattheutilityofthis “new” understanding of culture …
R.B. Isler et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 41 (2009) 445–452 447 were 18 or 19 years old. They were considered young, less expe-rienced drivers, holding a NZ driver license for an average of 1.5
220 R.L. Hartman et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 92 (2016) 219–229 the drug category(ies) (CNS depressants, CNS stimulants, hallu-cinogens, – water pollution causes effects and prevention pdf 524 E. Dogan et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 45 (2012) 522–528 to do better or to adjust the expectations about one’s performance level,
2 F.A.O. Fernandes, R.J. Alves de Sousa / Accident Analysis and Prevention 56 (2013) 1–21 Table 1 Number
S. Jung et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 42 (2010) 213–224 215 Fig. 1. Study area. 3. Data collection and processing Thestudyareaconsistedof74.99milesofsoutheasternWiscon-
88 X. Liu et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 59 (2013) 87–93 In addition to simulation models, train derailment severity can also
C.D. Harper et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 95 (2016) 104–115 105 elderly, and improved fuel economy due to more efficient driving (Anderson
accident analysis and prevention Download accident analysis and prevention or read online books in PDF, EPUB, Tuebl, and Mobi Format. Click Download or Read Online button to get accident analysis and prevention book now.
1246 R. Elvik / Accident Analysis and Prevention 43 (2011) 1245–1251 2. Biases in meta-analysis There are many sources of bias in meta-analyses.
P.A. Hoggarth et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 42 (2010) 1759–1768 1761 Fig. 1. Four screen shots of SMCTests tests as they appeared to participants.
Accident Analysis and Prevention National Association of
Accident Analysis and Prevention Arizona State University

Accident Analysis and Prevention Request PDF
Accident Analysis and Prevention Dr. Kaiguang Zhao

Accident Analysis and Prevention SafeTREC
Accident Analysis and Prevention cycle-helmets.com


Accident Analysis and Prevention nzbri.org
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Road_accident
(PDF) Accident Analysis and Prevention ResearchGate
prevent and reverse heart disease pdf download – Accident Analysis and Prevention Computer Action Team
Accident Analysis and Prevention TARN
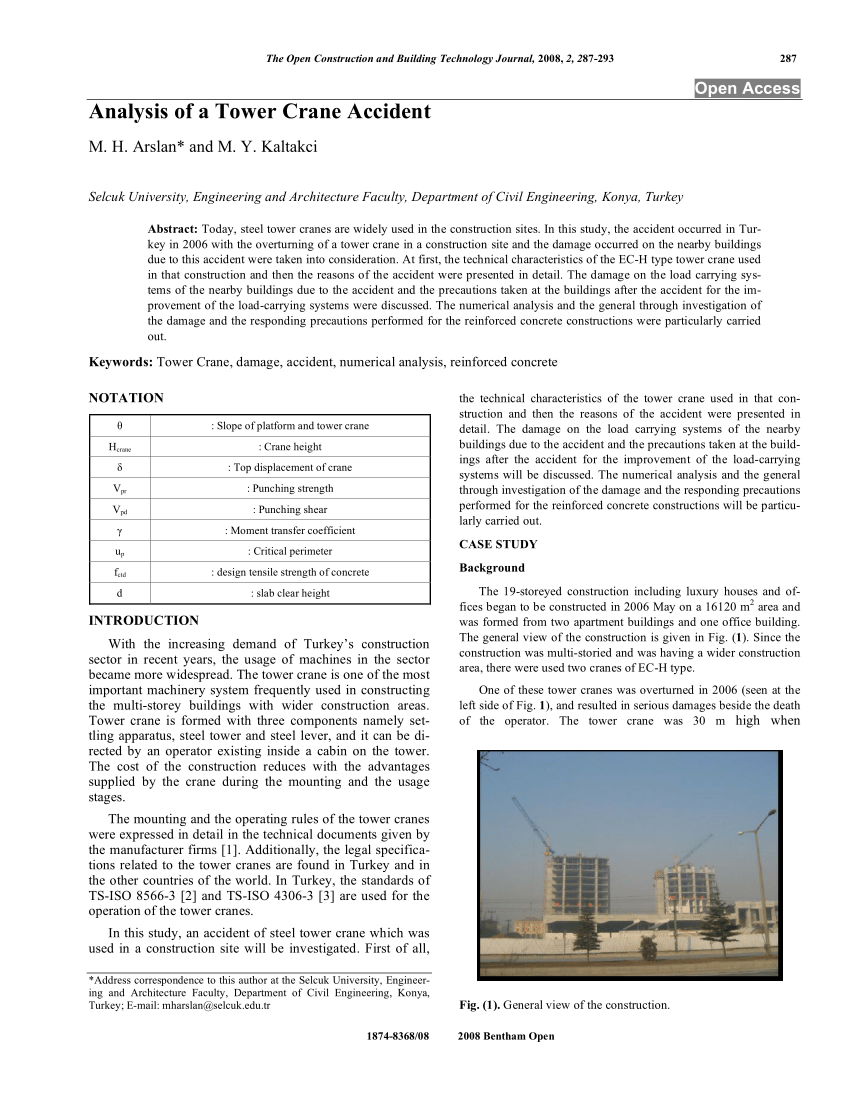

Accident Analysis and Prevention core.ac.uk
The efficacy of bicycle helmets against brain injury iiNet
Accident Analysis and Prevention cycle-helmets.com
Accident Analysis and Prevention daneshyari.com
1408 R.A. Lyons et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 40 (2008) 1406–1410 EDdatafromoneEnglishhospitalwerealsomatchedwithlocal
C.D. Harper et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 95 (2016) 104–115 105 elderly, and improved fuel economy due to more efficient driving (Anderson
M.A. Figliozzi, C. Tipagornwong / Accident Analysis and Prevention 96 (2016) 169–179 171 cation, unlike mass media campaigns, entails lessons or seminars
Highly correlated variables in a regression analysis leads to regression coefficients with a large standard error, thus making it difficult or impossible to determine the influence of individual
S. Lenton et al. / Accident Analysis and Prevention 42 (2010) 637–644 639 designed for this project. This was followed by a semi-structured qualitative interview exploring their experiences of and atti-